| |
In this short article I present my views regarding market and business requirements leading towards the 5G architecture.
Introduction
Digitalization, drones, virtualization, cloud, artificial intelligence, blockchain, (industrial) internet of things, autonomous vehicles etc. have become a layman’s term today.
|
These technologies are helping us enhance or, more correctly, optimize what we are already doing instead of creating something totally new. Result from this optimization is leading to opportunities for novel ideas to be generated leading to new value creation. New value creation in turn leads to betterment of society creating new business opportunities and profitability.
|
|
 |
Business Implications
These changes obviously impact the way we do business. It is well known that the value-chain concept is long gone.
|
One company or business being able to do everything is impossible which means that businesses have to work together to succeed in the market. This basically means that market has become flat where everyone has to work together. Although this might already be true in several industries, it has not been truly so in the telecommunications
|
|
 |
industry – the industry that is core of connectivity in the new era which will lead to new value creation and means for technology innovation.
Market Needs
Implications of this new era are many-fold, looking at it from 6 different perspectives:
- Optimization: Relates to several aspects including cost optimization that can be achieved by virtualized infrastructure (NFV) including cloud, network sharing and means to change partners easily for cost or functionality benefits etc.
- Variety: This is about several services that should be provisioned such as healthcare, industrial IoT etc. Besides that there are services for individuals and the variety of customers associated to each service.
- Personalization: Everyone, everything and every stakeholder is demanding services to be personalized as per their needs.
- Identity: Number of participants in the network will require unique identity for proper authentication that leads to charging. Here identity connects us to security credentials as well. It will be but obvious that there will be different types of identities in use bound to different types of credentials.
- Democratization: The new era of connectivity and technology enhancements we are in also means that everything should be available to everyone and everyone should have a say on how things are done.
- User space: This will be larger than ever seen before – from devices to people with different skills and experience bringing varying requirements.
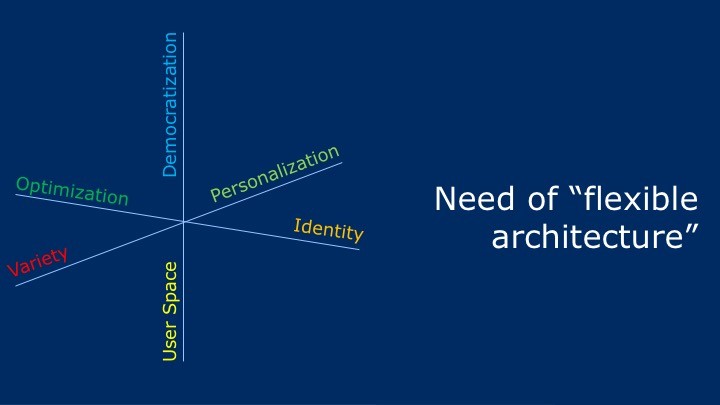
The above means that we are talking about an era of new business concepts and a flexible network, a network that allows everyone to work together, a network that can be unique per purpose (vertical instead of horizontal).
Introducing 5G
This is where 5G comes in, as a business concept and as a new flexible architecture. In 5G the demands of new era is mapped as:
- enhanced Mobile Broad-Band (eMBB): Fulfilling human centric use-cases, such as multimedia contents. With data-rates going up-to 20Gbps and delays down to 4ms.
- massive Machine Type Communication (mMTC): This is for IOT use-cases, e.g. temperature sensors, requiring large volume of devices with low volume of non-delay sensitive data meant for devices requiring battery life lasting 10 years.
- Ultra Reliable Low Latency Communication (URLLC): These are use-cases, e.g. autonomous vehicles, with stringent requirements on throughput, latency and availability. User plane latency is expected to be no more than 0.5ms.
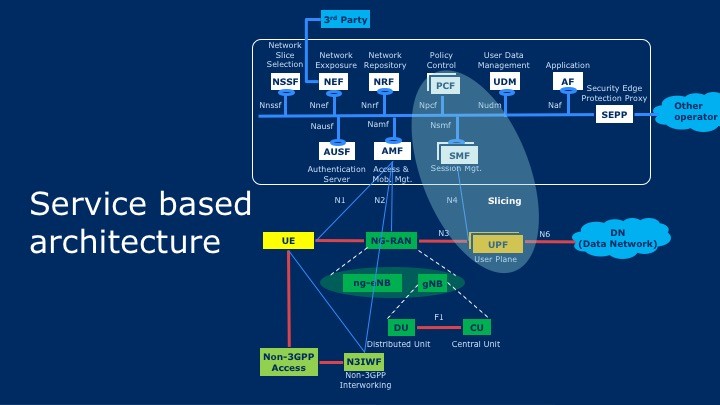
The Architecture
5G initial architecture by 3GPP is for eMBB, i.e. 5G Phase 1. Unlike earlier generations, within control-plane there is only service-based interface (SBI) that is based on well-known TLS, REST, HTTP, JSON etc. The network exposure function (NEF) gives connectivity to partners outside, security edge protection proxy (SEPP) is for secure connectivity to other operators while network slice selection function (NSSF) takes care of slice selection and the network repository function (NRF) is for discovery as well as authorization of communication between different function. The user data management (UDM) and authentication server function (AUSF) are, as the name says, for user data management and authentication respectively. The radio part is divided in central unit (CU) and distributed unit (DU) where the CU can connect to several DUs and reside on a cloud. One should note that there can be separate CU for user-plane and control-plane.
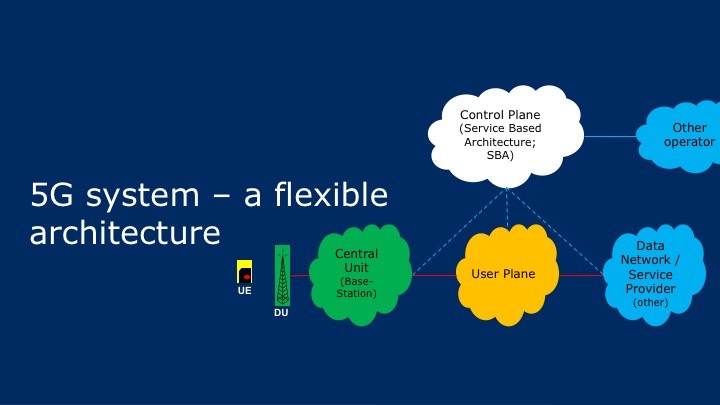
Opening Doors for Technology Innovation
The architecture is very modular. At a high level the modularization is provided by control- and user-plane separation.
|
|
|
Modularization also means that different parts or functions can be owned and managed by different stakeholders else at the minimum different stakeholders can have control over given functions for specific services. Multiple parties can play role by providing different functions (or same functions) of the architecture that is based on widely used technology |
running on cloud. With this it is obvious that the architecture fulfills the market needs – the 6 perspectives of the new era and more.
|
|
Interesting!
Many thanks
Thank you for this very informative article.
Team Celitech.