NAT 문서 모두 보기
오늘은 RFC 3489에서 정의하고 있는 NAT 타입 조사(NAT Behavior Discovery) 알고리즘에 대해 소개해 드리도록 하겠습니다.
본 내용을 이해하기 위해서는 아래 블로그글을 반드시 먼저 읽어 보시기 바랍니다.
1. NAT 장비는 이렇게 만들어야 하는데... (RFC 4787) - 1편: Mapping Behavior
2. NAT 장비는 이렇게 만들어야 하는데... (RFC 4787) - 2편: Filtering Behavior
3. STUN(RFC 3489)과 STUN(RFC 5389/5780)의 차이
NAT Type Discovery
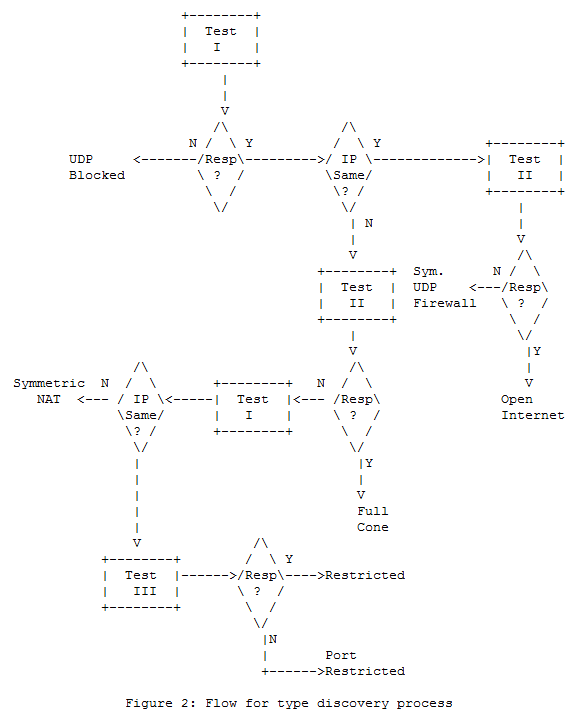
아래는 RFC 3489에서 설명하고 있는 NAT 타입 Discovery 알고리즘입니다.
10.1 Discovery Process
The flow makes use of three tests. In test I, the client sends a STUN Binding Request to a server, without any flags set in the CHANGE-REQUEST attribute, and without the RESPONSE-ADDRESS attribute. This causes the server to send the response back to the address and port that the request came from. In test II, the client sends a Binding Request with both the "change IP" and "change port" flags from the CHANGE-REQUEST attribute set. In test III, the client sends a Binding Request with only the "change port" flag set.
The client begins by initiating test I. If this test yields no response, the client knows right away that it is not capable of UDP connectivity. If the test produces a response, the client examines the MAPPED-ADDRESS attribute. If this address and port are the same as the local IP address and port of the socket used to send the request, the client knows that it is not natted. It executes test II.
If a response is received, the client knows that it has open access to the Internet (or, at least, its behind a firewall that behaves like a full-cone NAT, but without the translation). If no response is received, the client knows its behind a symmetric UDP firewall.
In the event that the IP address and port of the socket did not match the MAPPED-ADDRESS attribute in the response to test I, the client knows that it is behind a NAT. It performs test II. If a response is received, the client knows that it is behind a full-cone NAT. If no response is received, it performs test I (본 글에서는 test I'로 표시) again, but this time, does so to the address and port from the CHANGED-ADDRESS attribute from the response to test I. If the IP address and port returned in the MAPPED-ADDRESS attribute are not the same as the ones from the first test I, the client knows its behind a symmetric NAT. If the address and port are the same, the client is either behind a restricted or port restricted NAT. To make a determination about which one it is behind, the client initiates test III. If a response is received, its behind a restricted NAT, and if no response is received, its behind a port restricted NAT.
■ Test (Discovery) Procedure
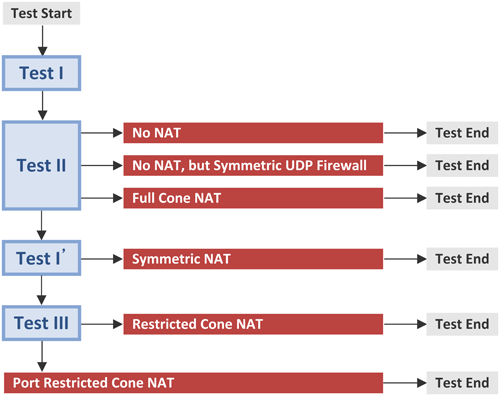
- Test II를 통해 NAT 혹은 Symmetric UDP Firewall 존재 유무 확인, Full Cone NAT 식별
- Test I'을 통해 Symmetric NAT 식별
- Test III를 통해 Restricted Con NAT 혹은 Port Restricted Cone NAT 식별
■ NAT/Firewall이 없는 경우 (Open Internet)
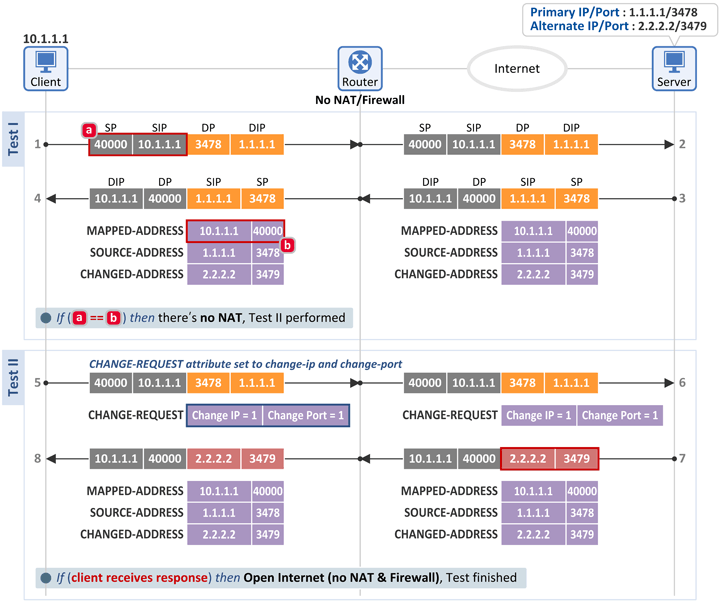
■ Test I
- 단말은 서버의 Primary IP:Primary Port(1.1.1.1:3478)로 Binding Request 메시지를 전송하고 그 응답으로 Binding Response 메시지를 수신합니다.
- 그리고 단말은 아래 2개의 필드를 비교하여 그 값이 동일하면 단말과 인터넷 사이에 NAT가 없다고 판단합니다.
- [a] Binding Request 메시지: IP 헤더 소스 정보 = 10.1.1.1:40000
- [b] Binding Response 메시지: MAPPED-ADDRESS attribute = 10.1.1.1:40000
- 서버는 Binding Request 메시지의 소스 정보[a]를 Binding Response 메시지의 MAPPED-ADDRESS[b]에 실어 단말로 전송하므로 이 2개의 값이 같다는 것은 NAT가 존재하지 않아 주소/포트 변환이 되지 않았다는 의미입니다.
■ Test II
- 그런 후 CHANGE-REQUEST attribute의 Change IP와 Change Port flag를 모두 1로 하여 Binding Request 메시지를 서버로 전송합니다.
- 이를 수신한 서버는 수신된 패킷의 Primary IP:Primary Port(1.1.1.1:3478)와 다른 주소/포트인 Alternate IP:Alternate Port(2.2.2.2:3479)를 소스 정보로 하여 Binding Response 메시지를 단말로 전송합니다.
- 만약 이 메시지를 수신하였다면 단말은 UDP Firewall이 없다고 판단합니다.
- 즉, Internal Address/Port(NAT에 의해 주소/포트 변환 전)와 External Address/Port(NAT에 의해 주소/포트 변환 후) 값이 동일하고, Outbound 패킷의 목적지 정보(1.1.1.1:3478)와 다른 소스 정보(2.2.2.2:3479)를 가진 Inbound 패킷이 통과(Allow)하였으므로 NAT/Firewall 모두 존재하지 않는 것입니다.
■ Symmetric UDP Firewall인 경우
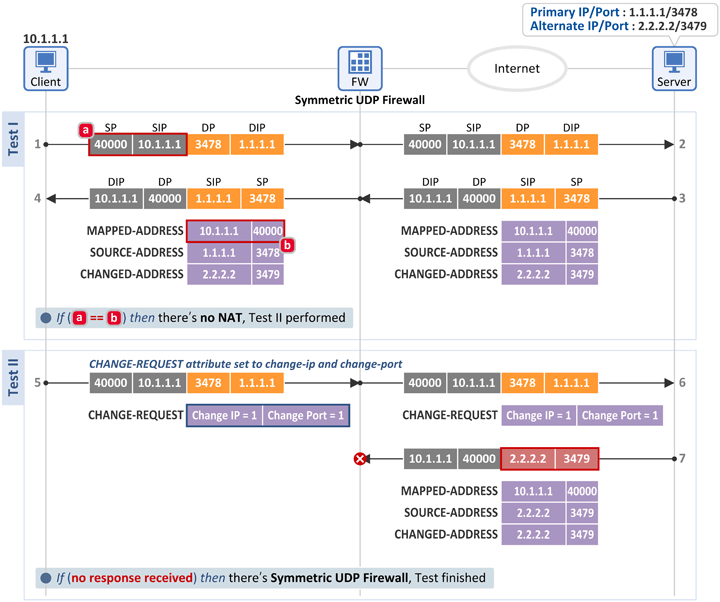
■ Test I
■ Test II
- 위(Open Internet) 시험과 동일한 Binding Request 메시지를 서버로 전송하는데 그 응답 메시지(Binding Response)를 수신하지 못하였습니다.
- 이 경우 단말은 UDP Symmetric Firewall이 존재한다고 판단합니다.
- 즉, Internal Address/Port와 External Address/Port 값이 동일하고, Outbound 패킷의 목적지 정보(1.1.1.1:3478)와 다른 소스 정보(2.2.2.2:3479)를 가진 Inbound 패킷이 폐기(Drop)되었으므로 NAT가 아닌 Firewall이 존재하는 것입니다.
■ Full Cone NAT인 경우
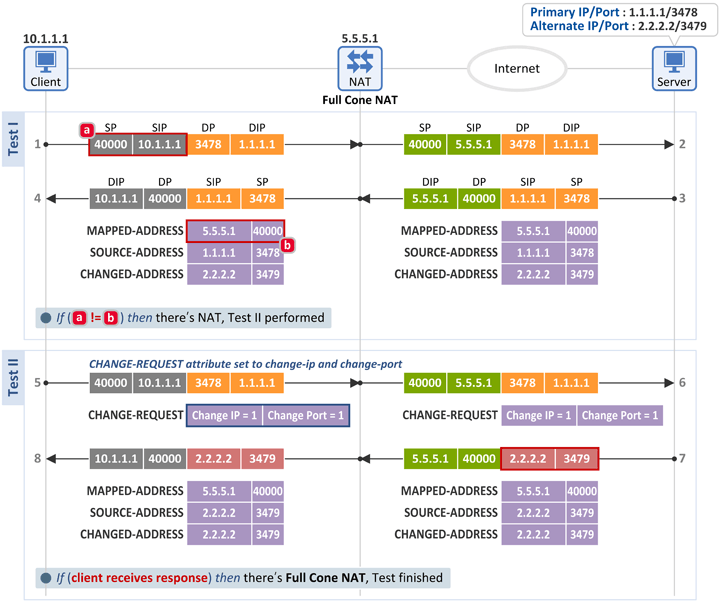
■ Test I
- 단말은 서버의 Primary IP:Primary Port(1.1.1.1:3478)로 Binding Request 메시지를 전송하고 그 응답으로 Binding Response 메시지를 수신합니다.
- 그리고 단말은 아래 2개의 필드를 비교하여 그 값이 같지 않으면 NAT가 존재한다고 판단합니다.
- [a] Binding Request 메시지: IP 헤더 소스 정보 = 10.1.1.1:40000
- [b] Binding Response 메시지: MAPPED-ADDRESS attribute = 5.5.5.1:40000
■ Test II
- 그런 후 CHANGE-REQUEST attribute의 Change IP와 Change Port flag를 모두 1로 하여 Binding Request 메시지를 서버로 전송합니다.
- 이를 수신한 서버는 수신된 패킷의 Primary IP:Primary Port(1.1.1.1:3478)와 다른 주소/포트인 Alternate IP:Alternate Port(2.2.2.2:3479)를 소스 정보로 하여 Binding Response 메시지를 단말로 전송합니다.
- 만약 이 메시지를 수신하였다면 단말은 Full Con NAT가 존재한다고 판단합니다.
- 즉, Internal Address/Port(10.1.1.1:40000)와 External Address/Port(5.5.5.1:40000)가 다르고, Outbound 패킷의 목적지 정보(1.1.1.1:3478)와 다른 소스 정보(2.2.2.2:3479)를 가진 Inbound 패킷을 허용(Allow)하였으므로 Full Cone NAT입니다. 뒤에서 설명할 Symmetric, Restricted Con, Port Restricted Con NAT의 경우 Outbound 패킷의 목적지 정보(1.1.1.1:3478)와 다른 Source IP(2.2.2.2) & Source Port(3479)인 Inbound 패킷을 폐기(Drop)합니다.
■ Symmetric NAT인 경우
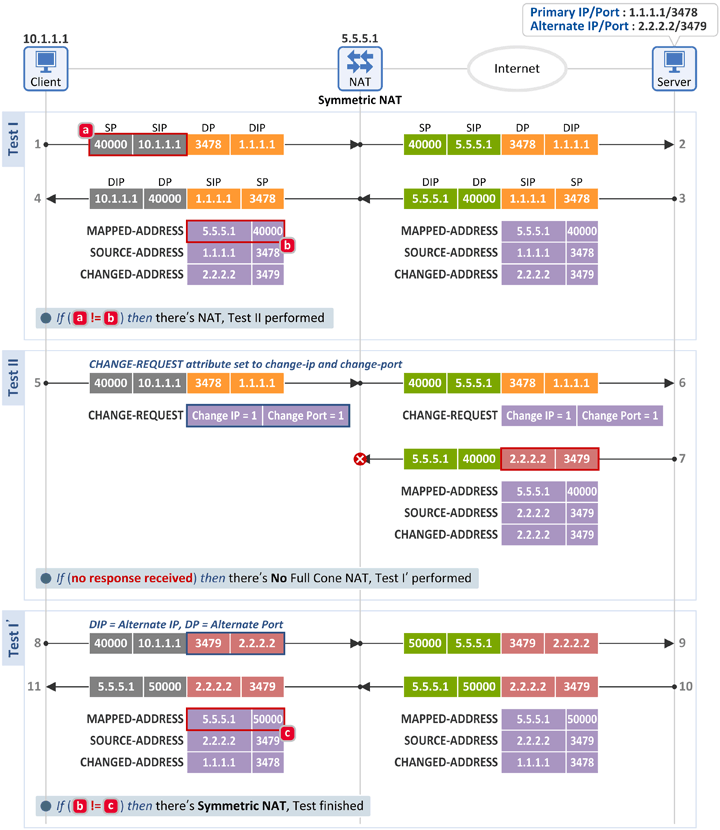
■ Test I
■ Test II
- Full Con NAT 시험과 동일한 Binding Request 메시지를 서버로 전송 하는데 그 응답 메시지(Binding Response)를 수신하지 못하였습니다.
- 이 경우 단말은 Full Cone NAT가 아니라고 판단하고 Test I'를 진행합니다.
■ Test I'
- 단말은 서버의 Alternate IP:Alternate Port(2.2.2.2:3479)를 목적지로 Binding Request 메시지를 전송하고 그 응답으로 Binding Response 메시지를 수신합니다.
- 그리고 단말은 아래 2개의 필드를 비교하여 그 값이 같지 않으면 Symmetric NAT가 존재한다고 판단합니다.
- [b] Binding Response 메시지: MAPPED-ADDRESS attribute = 5.5.5.1:40000
- [c] Binding Response 메시지: MAPPED-ADDRESS attribute = 5.5.5.1:50000
- 지난 시간의 RFC 3489와 RFC 5780 비교 설명에 의하면 NAT Mapping Behavior 관점에서 Full Con, Restricted Con, Port Restricted Con은 모두 Endpoint-Independent Mapping의 특성을 가지는 반면 Symmetric은 Address and Port-Dependent Mapping의 특성을 가집니다. 본 테스트를 통해 서로 다른 목적지 정보(1.1.1.1:3478과 2.2.2.2:3470)를 가진 2개의 패킷에 대해 서로 다른 External Port(40000과 50000)로 매핑 되었으므로 Symmetric NAT입니다.
■ Restricted Cone NAT인 경우
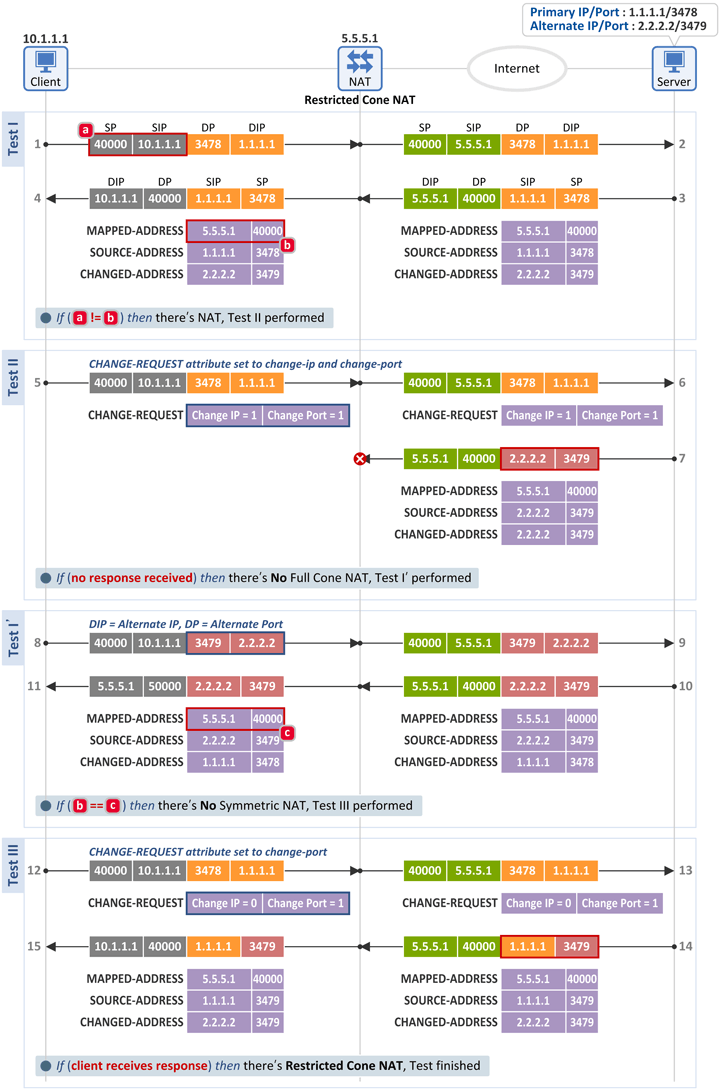
■ Test I
■ Test II
■ Test I'
- Symmetric NAT 시험과 동일한 Binding Request 메시지를 전송하고 그 응답으로 Binding Response 메시지를 수신합니다.
- 그리고 단말은 아래 2개의 필드를 비교하여 그 값이 동일하면 Symmetric NAT가 아니라고 판단하고 Test III를 진행합니다.
- [b] Binding Response 메시지: MAPPED-ADDRESS attribute = 5.5.5.1:40000
- [c] Binding Response 메시지: MAPPED-ADDRESS attribute = 5.5.5.1:40000
■ Test III
- 단말은 서버의 Primary IP:Primary Port(2.2.2.2:3479)를 목적지로 하여 Binding Request 메시지를 전송하는데 그 때 CHANGE-REQUEST attribute의 Change Port flag를 1로 합니다.
- 그러면 서버는 소스 정보를 Primary IP:Alternate Port(1.1.1.1:3479)로 하여 Binding Response 메시지를 단말로 전송하게 되며, 만약 이 메시지를 수신하였다면 단말은 Restricted Con NAT가 존재한다고 판단합니다.
- 즉, Outbound 패킷과 "동일 Destination IP & 다른 포트"를 소스 정보(1.1.1.1:3479)로 한 Inbound 패킷을 허용(Allow)하였으므로 Restricted Con NAT입니다.
■ Port Restricted Cone NAT인 경우
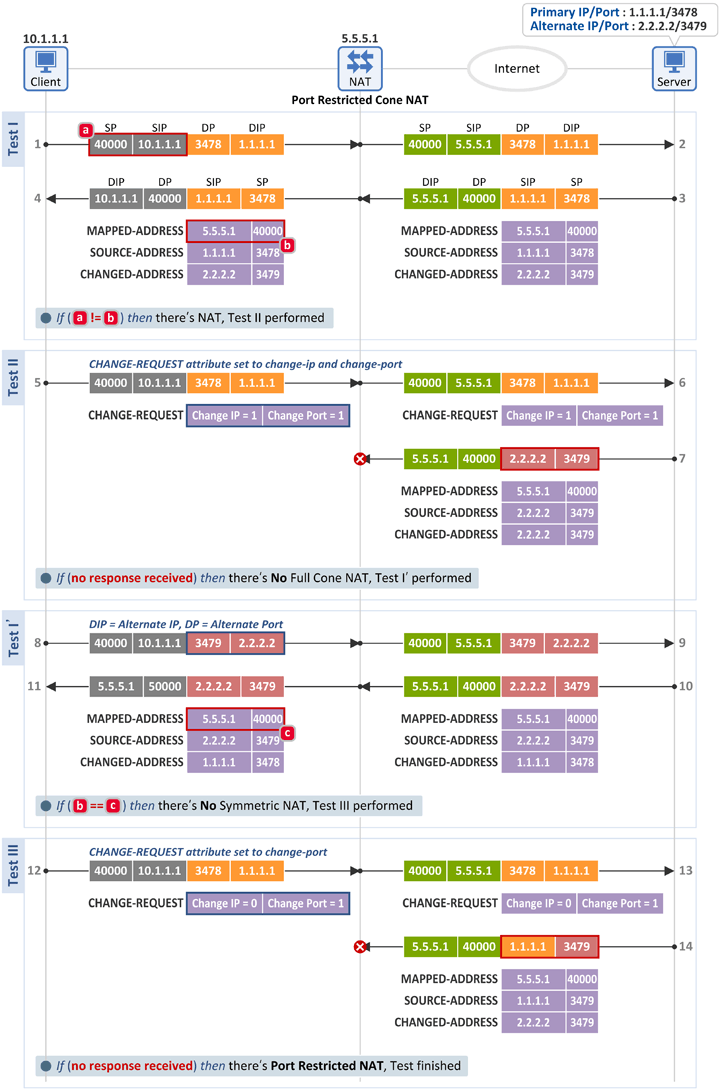
■ Test I
- Restricted Con NAT 시험과 동일
■ Test II
- Restricted Con NAT 시험과 동일
■ Test I'
- Restricted Con NAT 시험과 동일
■ Test III
- Restricted Con NAT 시험과 동일한 Binding Request 메시지를 전송하는데 그 응답 메시지(Binding Response)를 수신하지 못한 경우, 단말은 Port Restricted Con NAT가 존재한다고 판단합니다.
- 즉, Outbound 패킷과 "동일 Destination IP & 다른 포트"를 소스 정보(1.1.1.1:3479)로 한 Inbound 패킷을 폐기(Drop)하였으므로 Restricted Con NAT입니다.
RFC 3489 NAT Behavior Discovery Tool 소개
□ Test: ipTIME N2E를 대상으로 STUNTMAN과 JSTUN을 이용하여 NAT Type을 시험
□ Test Result: Port Restricted Con NAT