| |
1. Definition
The AF and the Rx interface between the PCRF and AF are defined in the 3GPP specifications and they are mainly used by the PCRF to connect third-party applications (for example, OTT) and IMS networks to implement PCC-based VoLTE. The section describes only the Embedded PCRF capability in the VoLTE solution.
2. Benefits
Benefits to Carriers:
This feature helps carriers to use PCC-based VoLTE solution to implement IP link–based high-quality voice and video calls on the LTE network.
Benefits to End Users:
This feature enables subscribers to make high-quality voice and video calls on LTE networks.
3. Description
In the 3GPP specifications, the IMS is defined as a part of the LTE core network. After carriers use the LTE + IMS core network, PCC-based VoLTE solution can be used.
In this solution, the Embedded PCRF connects to the P-CSCF through the Rx interface and to the P-GW through the Gx interface.
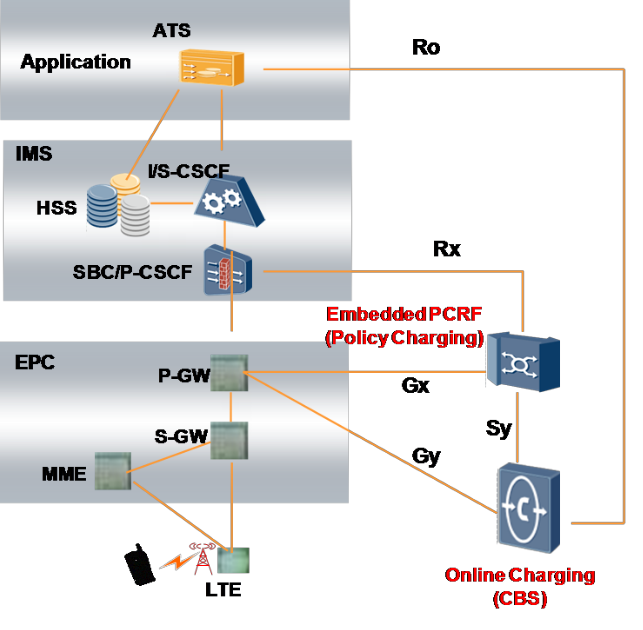
Figure 1. VoLTE solution network diagram
4. IMS Common Call
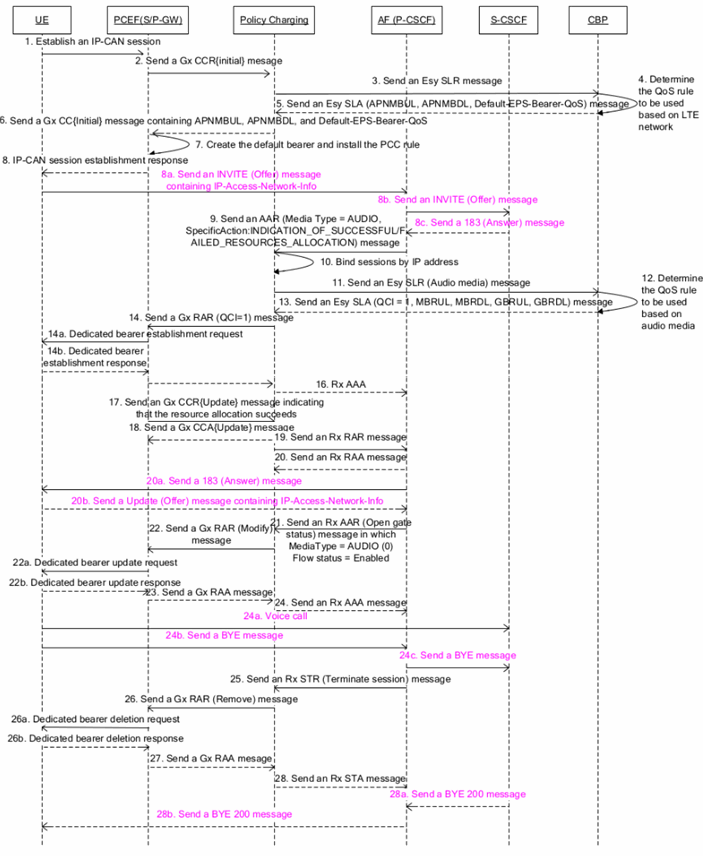
Figure 2. IMS common call process
- A subscriber attempts to make an IMS common call through E-URAN. The UE sends a request to the PCEF to establish an IP-connectivity access network (IP-CAN) session.
- The PCEF sends a CCR{Initial} message containing the subscriber ID and access network information to the Policy Charging through the Gx interface.
- The Policy Charging sends an SLR message containing the subscriber ID and network information reported in the Gx interface to the CBP through the Esy interface.
- The CBP generates a PCC rule (key parameters: QCI whose value is 5, ARP, APNMBUL, and APNMBDL) based on the subscriber's subscription and network information.
- The CBP sends an SLA message containing the PCC rule to the Policy Charging through the Esy interface.
- The Policy Charging sends a CCA{Initial} message containing the PCC rule to the PCEF through the Gx interface.
- The PCEF creates a default bearer based on the authorization result and installs the PCC rule.
- The PCEF sends an IP-CAN Establish Response message to the UE.
- The AF sends an AAR message to the Policy Charging through the Rx interface to establish a dedicated bearer for the voice media stream. The AAR message contains the subscriber ID, AF ID, IMS application layer charging ID, and media information (including the media type and media stream description).
- The Policy Charging binds the AF session to the corresponding IP-CAN session based on the subscriber IP address in the AAR message.
- The Policy Charging sends an SLR message containing the received voice media stream to the CBP through the Esy interface.
- The CBP generates a PCC rule (key parameters: QCI whose value is 1, ARP, GBR, and MBR) for the voice media stream based on the subscriber's subscription information.
- The CBP sends an SLA message containing the PCC rule to the Policy Charging through the Esy interface.
- The Policy Charging sends an RAR message containing the PCC rule to the PCEF through the Gx interface.
- The PCEF searches for the dedicated bearer based on QCI or ARP in the PCC rule. If no dedicated bearer is found, the PCEF creates a dedicated bearer, installs the voice media stream information and PCC rule in the dedicated bearer, and sends an RAA message to the Policy Charging through the Gx interface.
- The Policy Charging sends an AAA message to the AF through the Rx interface. The dedicated bearer is successfully created for the voice media stream.
- The PCEF sends a CCR{Update} message to the Policy Charging through the Gx interface, notifying the Policy Charging that the resource is successfully reserved.
- The Policy Charging sends a CCA{Update} message to the PCEF through the Gx interface.
- The Policy Charging sends an RAR message to the AF through the Rx interface, indicating that the resource is successfully reserved.
- The AF sends an RAA message to the Policy Charging through the Rx interface.
- The AF receives an INVITE 200 message and sends an AAR message to the Policy Charging through the Rx interface to enable bearer gating control.
- The Policy Charging sends an RAR message to the PCEF through the Gx interface, instructing the PCEF to modify bearer information about the voice media stream.
- Note: If a subscriber makes a VoLTE voice call after gating control is enabled, the VoLTE voice media stream is transmitted through the dedicated bearer to ensure the QoS.
- The PCEF updates the voice media stream status and sends an RAA message to the Policy Charging through the Gx interface.
- The Policy Charging sends an AAA message to the AF through the Rx interface. The voice call is connected.
- The subscriber releases the call. The AF sends an STR message to the Policy Charging through the Rx interface to terminate the bearer session.
- The Policy Charging sends an RAR message to the PCEF through the Gx interface, instructing the PCEF to delete the dedicated bearer of the voice media stream. The PCEF deletes the dedicated bearer.
- The PCEF sends an RAA message to the Policy Charging through the Gx interface.
- The Policy Charging deletes the Rx session and sends an STA message to the AF through the Rx interface. The process of deleting the dedicated bearer of the voice media stream is complete.
5. IMS Emergency Call
The Policy Charging supports IMS emergency calls, for example, calls to 911.
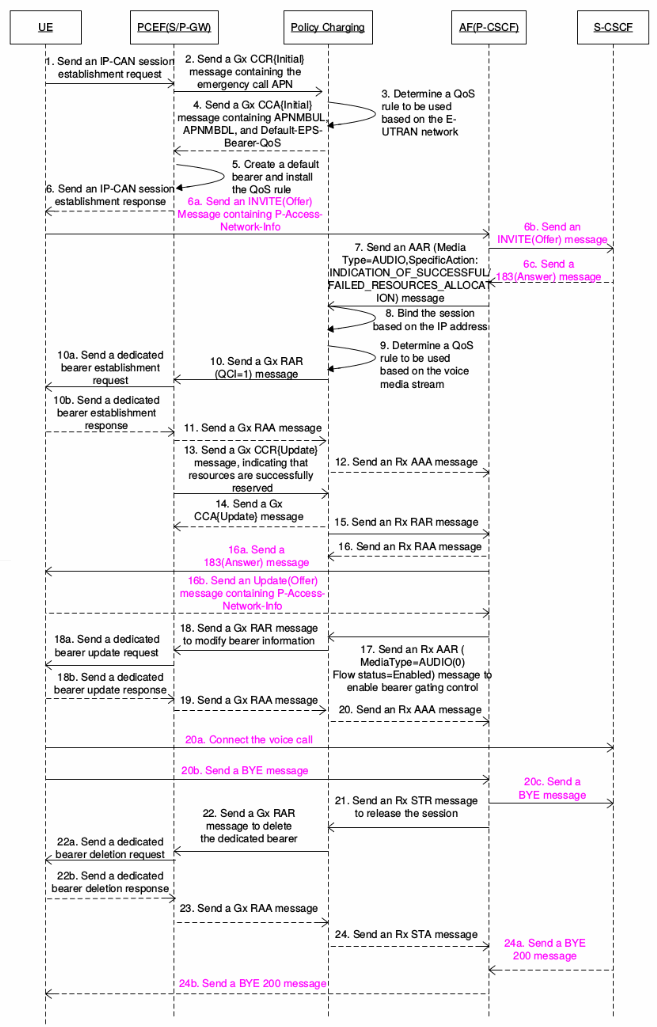
Figure 3. IMS emergency call process
- A subscriber attempts to make an IMS emergency call through the emergency call APN. The UE sends a request to establish an IP-CAN session.
- The PCEF sends a CCR{Initial} message containing information such as the access network and emergency call APN to the Policy Charging through the Gx interface.
- Note: The emergency call APN must be configured in the PCEF to ensure that sessions initialized by the emergency call APN are not restricted by flow control or license and have the highest priority.
- Note: If the Policy Charging finds a Gx session indicating the emergency call service, the emergency call flag is added to the stored session information. The Policy Charging does not check the subscriber number in sessions matching the emergency call service because the sessions may not contain any subscriber numbers.
- The Policy Charging generates a PCC rule (key parameters: QCI whose value is 5, ARP, APNMBUL, and APNMBDL) based on the emergency call APN.
- Note: To establish an IP-CAN session for an emergency call APN, a default global policy must be configured in the PCRF for creating the default emergency call bearer.
- Note: The CCR{Initial} message sent through the Gx may not contain information such as subscriber IMSI because the subscriber may not belong to the local carrier. In this case, the global default policy configured in the Policy Charging is used for authorization.
- The Policy Charging sends a CCA{Initial} message containing the PCC rule to the PCEF through the Gx interface.
- The PCEF creates a default bearer based on the authorization result and installs the PCC rule.
- The PCEF sends an IP-CAN Establish Response message to UE.
- Based on the requested destination address, the AF determines that the call is an emergency call and sends an AAR message to the Policy Charging through the Rx interface.
- Note: In addition to the emergency call AF ID, IMS application layer charging ID, and media information (including the media type and media stream description), the AAR message sent through the Rx interface needs to contain the Service-URN AVP, which is used to indicate an emergency call session.
- The Policy Charging binds the AF session to the corresponding IP-CAN session based on the subscriber IP address in the AAR message.
- Note: The IP-CAN session for the emergency call APN allows only IMS emergency calls. When receiving an AAR message without the Service-URN AVP through the Rx interface, the Policy Charging rejects the request and returns error code NAUTHORIZED_NON_EMERGENCY_SESSION.
- The Policy Charging generates a PCC rule (key parameters: QCI, ARP, GBR, and MBR) for the voice media stream.
- Note: For the emergency call service, the ARP parameter must be set to the highest priority.
- The Policy Charging sends an RAR message containing the PCC rule of the voice media stream to the PCEF through the Gx interface. The PCEF searches for the dedicated bearer based on QCI or ARP in the PCC rule. If no dedicated bearer is found, the Policy Charging creates a dedicated bearer and installs the voice media stream information and PCC rule in the dedicated bearer.
- The PCEF sends an RAA message to the Policy Charging through the Gx interface.
- The Policy Charging sends an AAA message to the AF through the Rx interface. The dedicated bearer is successfully created for the voice media stream.
- The PCEF sends a CCR{Update} message to the Policy Charging through the Gx interface, notifying the Policy Charging that the resource is successfully reserved.
- The Policy Charging sends a CCA{Update} message to the PCEF through the Gx interface.
- The Policy Charging sends an RAR message to the AF through the Rx interface, indicating that the resource is successfully reserved.
- The AF sends an RAA message to the Policy Charging through the Rx interface.
- The AF receives an INVITE 200 message and sends an AAR message to the Policy Charging through the Rx interface to enable bearer gating control.
- The Policy Charging sends an RAR message to the PCEF through the Gx interface, instructing the PCEF to modify bearer information about the voice media stream.
- The PCEF updates the voice media stream status and sends an RAA message to the Policy Charging through the Gx interface.
- The Policy Charging sends an AAA message to the AF through the Rx interface. The voice call is connected.
- The subscriber terminates the call. The AF sends an STR message to the Policy Charging through the Rx interface to terminate the bearer session.
- The Policy Charging sends an RAR message to the PCEF through the Gx interface, instructing the PCEF to delete the dedicated bearer of the voice media stream. The PCEF deletes the dedicated bearer.
- The PCEF sends an RAA message to the Policy Charging through the Gx interface.
- The Policy Charging deletes the Rx session and sends an STA message to the AF through the Rx interface. The process of deleting the dedicated bearer of the voice media stream is complete.
|
|
Two queries:
1) In Call flow "4. IMS Common Call", after establishing default bearer, the call flow shows that UE sends INVITE. I believe, INVITE would be sent on a dedicated bearer with QCI 5. How does that dedicated bearer is created?
2) Assume dedicated bearer is created with QCI 5. How does INVITE received at PCEF reaches an AF? Is there a direct connection between AF and PCEF?
Thanks
thanks to review this post.
The answer for question 2:
This is Huawei Solution, and as you may know, S/P GW in EPC core play role as PCEF to Enforce the PCCs.
In Figure 1. VoLTE solution network diagram, the PCEF (S/PGW) has directly connection to P-CSCF as AF.
the Answer of Question1, I need more time to check.
Hi ,
Let's assume , we got 10 000 connecitons/IP-CAN sessions already established (dedicated bearer for VoLTE), what happen once I loose Gx interface? What will happen with current sessions? What will be with new requests?
Thank you in advance
Hi ,
Good article !
You have mentioned that OTT ( say whatsapp , viber etc ) applications also use Rx , i have 2 queries on the same :-
1 . OTT applications run on default bearer and use default bearer QOS( which is low ) , am i correct on this ?
Can Rx interface ( which is used by P-cscf for creating new dedicated bearer ) be used here ?
Are you talking about scenario where OTT and Operator join hands and that OTT server acts as a AF ? are there any specs I can refer for this ?
2 . Can AF over Rx interface disable an IP flow on default bearer , to elaborate , Is it possible for AAR message from AF with ( flow description = IP address and port of a server and port ) can disable this server IP and Port , which is on default bearer .
Thank you for you help in advance.
Regards,
Sj
Yes. the OTT Application runs on default bearer and using the QOS.
The PCEF checks whether any dedicated bearer meets the requirement specified in the QoS rule.− If a dedicated bearer is available, the PCEF installs the media stream information and
− If a dedicated bearer is available, the PCEF installs the media stream information and the QoS rule on this bearer and sends an RAA message to the PCRF.
− If no dedicated bearer is available, the PCEF establishes a dedicated bearer, installs the media stream information and the QoS rule on this bearer, and sends an RAA message to the PCRF.
The Application Function (AF) (eg. P-CSCF for IMS solution) interacts with applications or services that require dynamic PCC. The AF extracts session information from the application signaling and provides it to the PCRF over the Rx interface.
refer to ETSI TS 129 213 V11.4.0 for Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; Policy and charging control signaling flows and Quality of Service (QoS) parameter mapping (3GPP TS 29.213 version 11.4.0 Release 11)
HI all how the IMS and EPC binding takes place using which KEY parameter. I mean between AAR/RAR to CREATE BEARER REQUEST.
i tried to map with ipv6 vs TFT but some times TFT is repeating ?
Please have look to below: (note: PCRF called by Huawei UPCC)
Message flow for QoS control over dedicated bearers:
6. The UPCC binds the AF session to an IP-CAN session based on the IP address contained in the AAR message and finds the corresponding PCEF. Then, the UPCC generates a QoS rule based on the information contained in the AAR message and the service policy and subscription data stored in the UPCC. The UPCC delivers the media stream information and QoS rule to the PCEF in a Re-Auth-Request (RAR) message. The QoS rule contains the key parameters QCI, ARP, GBR, and MBR. In the RAR message, the QCI is set to 1, indicating that the requested bearer is a dedicated bearer.
7. The PCEF checks whether any dedicated voice bearer satisfies the QoS rule.
− If a dedicated voice bearer satisfies the QoS rule, the PCEF installs the media stream information and the QoS rule on this bearer and sends a Re-Auth-Answer (RAA) message to the UPCC.
− If no dedicated voice bearer satisfies the QoS rule, the PCEF establishes a new dedicated voice bearer, installs the media stream information and the QoS rule on this new bearer, and sends an RAA message to the UPCC.
...
14. After the UPCC receives the AAR message, it enables the Bearer Gate function when updating policies and sends an RAR message to the PCEF, instructing the PCEF to modify the bearer information.
15. After the PCEF receives the RAR message, it modifies the bearer information, updates the media stream information, and sends an RAA message to the UPCC.
...
18. The UPCC deletes the media stream information and sends an RAR message carrying Remove QoS Rules to instruct the PCEF to delete the dedicated voice bearer.
19. The PCEF deletes the dedicated voice bearer and sends an RAA message to the UPCC.
Hi,
I have a question,while in Figure 2. (IMS common call process) step 25~26,I want to know how pcrf send remov PCC to PCEF?While STR(AF->PCRF) did not contain any media or policy information,PCRF how to know whic PCC should be sent to PCEF to remov.
I would be greatfull for your reply!
Thanks!
Hi Anne,
you need to have Rx and Gx session in a database, the key is Framed-IP-Adress. Then you will know which rules PCRF have issued...
When AAR send from AF to PCRF at that time which parameters will check by the PCRF from AAR request and how it will be detected and find the details to send RAR message to Gateway.
What is the main AVP to check by PCRF from the AAR request?
When AAR sends from AF to PCRF at that time which parameters will check by the PCRF from AAR request and how it will be detected and find the details to send RAR message to Gateway.
What is the main AVP to check by PCRF from the AAR request?
Hi,
Very good article indeed.
You mentioned about "The section describes only the Embedded PCRF capability in the VoLTE solution." What other kind of deployment of PCRF with S/P-GW , do you suggest?
Thanks in advance,
AS
Hi A very Good article , I have a Small Doubt regarding flow Description.
1) If the Flow Description comes as "Permit IN" should PCRF change it to "Permit OUT" In case of UPLINK flowdirection while sending it towards Gx?
2) Also if the Destination IP sent by Rx is "Any" , Can PCRF forward the same "Any" in destination Ip towards Gx? The Question behind this is from this spec point (5.3.54 of 3GPP TS 29.212) towards Gx
Destination IP address (possibly masked). The Destination IP address shall be derived from the packet filter
parameters sent by the UE. The Destination shall be set to the value provided by the UE. If no Destination IP
address is provided in the packet filter the Destination shall be set to "assigned", which refers to the Ipv4 address
and/or Ipv6 prefix of the UE as indicated by the Framed-IP-Address and/or Framed-Ipv6-Prefix AVPs.
But a Contridicting point is available for Rx from Spec
5.3.8 Flow-Description AVP
The Flow-Description AVP (AVP code 507) is of type IPFilterRule, and defines a packet filter for an IP flow with the following information:
- Direction (in or out). The direction "in" refers to uplink IP flows, and the direction "out" refers to downlink IP flows.
- Source and destination IP address (possibly masked).
- Protocol.
- Source and destination port.
The IPFilterRule type shall be used over Rx interface with the following restrictions:
- The Source Port may be omitted to indicate that any source port is allowed. Lists or ranges shall not be used.
- Only the Action "permit" shall be used.
- No "options" shall be used.
- The invert modifier "!" for addresses shall not be used.
- The keyword "assigned" shall not be used.
Is there any sample pcap availaible to check messages communicating on rx interface