I. Introduction
As we need a phone number to make a call to someone, we need an address to communicate with a network host over the Internet. This address is called an "Internet Protocol (IP) address". Generally, IP addresses are dynamically allocated to clients accessing the Internet, through Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP), a protocol designed for dynamic allocation of IP addresses, as defined in [1].
DHCP adopts the concept of a “lease” in IP allocation. This means, a DHCP server does not allocate an IP address to a client permanently. What it does instead is set a “lease duration” and allow the client to use the allocated IP address only during the set lease duration. If the client wishes to use the allocated IP address for longer than the lease duration, it should request the DHCP server for renewal of the lease. If not, it performs an IP address release procedure instead.
This document is organized as follows: Chapter II will explain the procedure for allocating/leasing IP addresses, and Chapter III and Chapter IV will describe the procedure for extending the lease time of, and releasing allocated IP addresses, respectively. Chapter V will summarize all DHCP procedures covered in the previous chapters. Finally, in Appendices, specific message parameters used in each DHCP procedure will be discussed.
II. IP Address Allocation/Lease Procedure
As shown in Figure 1 below, the following four basic phases are required in DHCP operations between a DHCP server and DHCP client (e.g. a PC) in order for the client to get/lease network configuration data, such as IP address from the DHCP server.
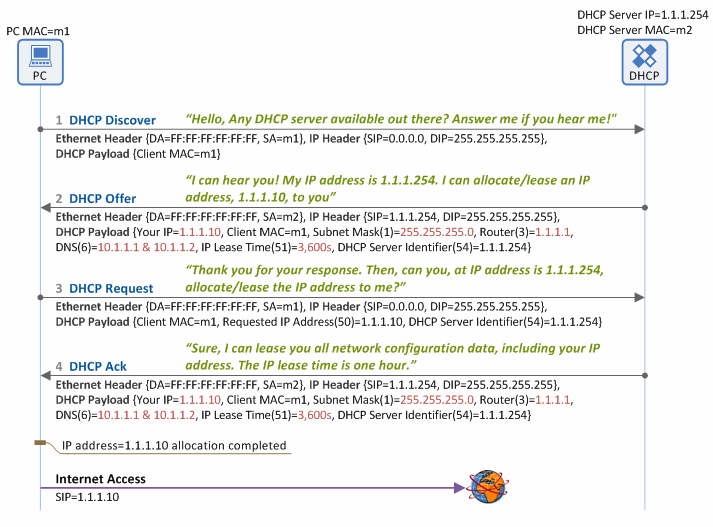
Figure 1. IP address allocation/lease procedure using DHCP
1. DHCP Discover
When a client (PC) is booted, it broadcasts a DHCP Discover message over the Ethernet network to locate all available DHCP servers on the same subnet network (by setting the destination MAC address in the Ethernet header as Broadcast MAC=FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF), reaching all the DHCP servers on the same subnet network.
2. DHCP Offer
When a DHCP server receives the DHCP Discover message from the client, it also broadcasts a DHCP Offer message over the Ethernet network (because the client IP address has not been allocated yet), informing the client that it is available. This message contains the network information, such as client IP address, subnet mask, default gateway IP address, DNS IP address, IP lease time and DHCP server IP address. The DHCP Offer message broadcasted is delivered to all the clients on the same subnet network, including the one that sent the DHCP Discover message.
3. DHCP Request
The client, having received the DHCP Offer message, recognizes there is a DHCP server available on the same subnet. Then it broadcasts a DHCP Request message to the server over the Ethernet network, requesting network configuration data including an IP address for itself. If more than one DHCP server responds on the same subnet and hence the client receives multiple DHCP Offer messages, it selects one of the DHCP servers, and enters the IP address of the selected DHCP server in the DHCP Server Identifier (option 54) field of the DHCP Request message. Then it informs all the DHCP servers on the subnet network about such selection by broadcasting the DHCP Request message. Typically, all DHCP servers internally store the network configuration data (i.e. IP address for the client and other information) when they send a DHCP Offer message. So, the client broadcasts the DHCP Request message to all the DHCP servers, so that those not selected can also receive the message and delete the stored network configuration data from their memory.
4. DHCP Ack
The DHCP server which received the DHCP Request message from the client checks if the IP address shown in the DHCP Server Identifier (option 54) field matches its own. If it does, it broadcasts a DHCP Ack message ensuring the client can receive the message (Note: the client has NOT been allocated an IP address yet).
At this time, the DHCP server transfers all the network configuration data including the client IP address – the same data sent along with the DHCP Offer message - to the client. Then the client configures a network interface using the transferred data, finally connecting to the Internet. The typical network configuration data includes:
- IP address
- Subnet mask
- Default gateway IP address
- DNS server IP address
- Lease time (during which a client can use the IP address allocated/leased by a DHCP server)
The Figure 2 shows the network configuration of a PC client (Windows 7) of which IP allocation procedure is completed.
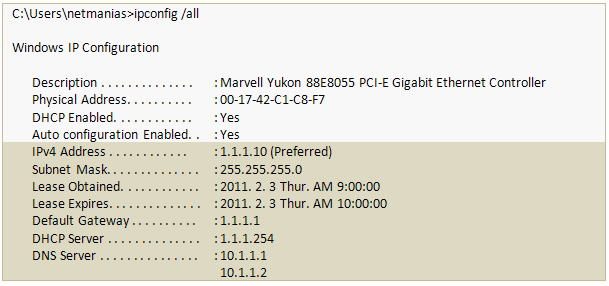
Figure 2. Network configuration of a PC client (Windows 7)
III. IP Address Renewal Procedure
A DHCP Ack message is the last message sent in the “IP address allocation/lease” procedure. It contains the IP Lease Time (option 51) parameter, and a client can use an allocated IP address (e.g. 1.1.1.10 in Figure 3) only for the time period (lease duration) specified in the option parameter. Thus, to use the IP address beyond the lease duration, the client has to request approval from the DHCP server to renew the IP address as shown in Figure 3.
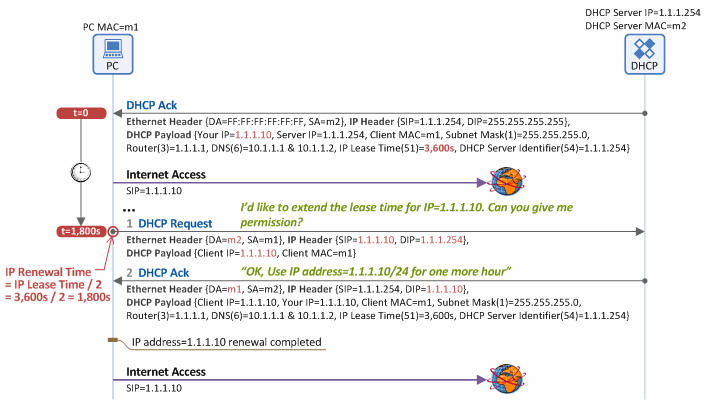
Figure 3. IP address lease renewal procedure using DHCP
1. DHCP Request
In Figure 3, the lease time is given as 1 hour. When half of it has passed (i.e. 1,800 seconds/30 minutes in Figure 3), the client sends a DHCP Request message to the DHCP server to renew its lease time (Note: In case of IP renewal, no DHCP Discover/Offer process is required). Unlike in the IP address allocation/lease procedure, the client does not broadcast the DHCP Request message (Destination MAC=FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF, Destination IP=255.255.255.255), but unicasts it (Destination MAC=DHCP Server MAC (m2), Destination IP=DHCP Server IP (1.1.1.254)). That is because the DHCP server and client have already known each other’s IP address. The DHCP Request message for IP address renewal should include the IP address of the client requesting the renewal in the “Client IP Address (ciaddr)” field, but should exclude Requested IP Address (option 50) and DHCP Sever Identifier (option 54) fields.
2. DHCP Ack
Upon accepting the DHCP Request message (for IP address renewal) received from the client, the DHCP server also unicasts, and does not broadcast, a DHCP Ack message (Destination MAC=PC MAC (m1), Destination IP=PC IP (1.1.1.10)), including network configuration data such as the client IP address, subnet mask, default gateway IP address, DNS IP address and lease time, to the client. Once this process is completed, the client can keep its current IP address for the extended lease time as specified in the DHCP Ack message.
IV. IP Address Release Procedure
When a client is shut down gracefully,1 or ‘ipconfig/release’ command is entered in the DOS command window of Windows, the client unicasts a DHCP Request message to the DHCP server in order to return its allocated IP address, as seen in Figure 4. Then it releases the network configuration data (i.e. client IP address, subnet mask, default gateway IP address, DNS IP address, etc.), consequently having no access to the Internet any more.
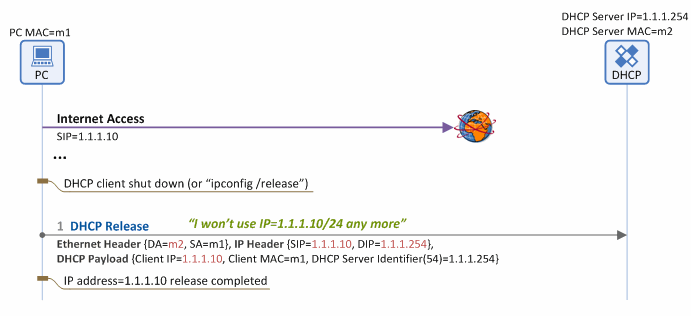
Figure 4. IP address release procedure using DHCP
1. DHCP Release
If the client does not need its allocated IP address any longer, it unicasts a DHCP Release message (Destination MAC=DHCP Server MAC (m2), Destination IP=DHCP Server IP (1.1.1.254)) to the DHCP server. The server then releases the client IP address (1.1.1.10) listed in the Client IP field of the received message.
V. Summary
This chapter summarizes the basic DHCP procedures: 1) IP address allocation/lease, 2) IP address renewal and 3) IP address release. Figure 5 shows a message flow diagram illustrating all these DHCP procedures.
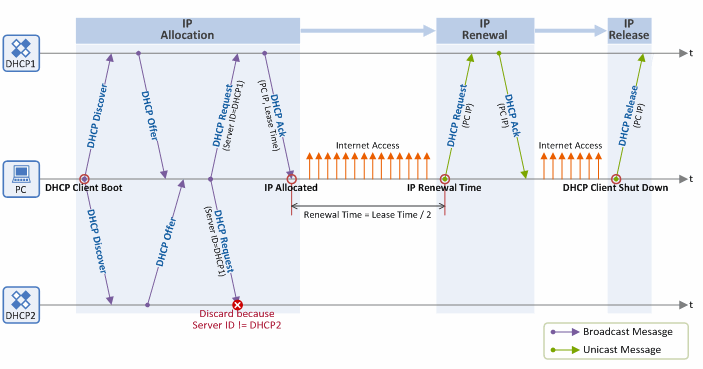
Figure 5. Summary of DHCP protocol procedures
- IP address allocation/lease: Once a DHCP client is booted up, it broadcasts a DHCP Discover message, and in respond to the message, a DHCP server broadcasts a DHCP Offer message. In case there is more than one DHCP server on the subnet, the client selects one of the servers, and broadcasts a DHCP Request message with the information of the selected server entered in the DHCP Server Identifier (option 54) field. Finally, the client receives network configuration data such as client IP address, subnet mask, default gateway IP address, DNS IP address, IP lease time from the server, and configures its network interfaces using the data.
- IP address renewal: When half of the lease time set through “IP address allocation/lease” procedure has passed, it unicasts a DHCP Request message to the DHCP server for renewal of its IP address. The DHCP server, upon receiving the DHCP Request message, accepts the request by responding with a unicast DHCP Ack message.
- IP address release: Once the client is logged-off, it returns the allocated IP address to the DHCP server by unicasting a DHCP Release message to the DHCP server.
VI. Closing
This document is the first in our technical documents series about DHCP and has so far explained the basic operations of DHCP. It has covered only the fundamentals and will be used as a reference for subsequent technical documents in the DHCP series.
The DHCP technical documents series will cover the following topics:
- Detailed DHCP technology defined in RFC 2131.
- Concept of DHCP Relay Agent and DHCP Proxy Agent.
- Client IP address allocation procedure through DHCP in operator networks (Note: Many telecom operators are facing issues with subscriber identification and authentication, DHCP security, DHCP message broadcasting, etc.).
- Plan for integrated management of IP address in an enterprise or in a distributed enterprise network having a head office and multiple branches.
References
[1] R, Droms, “Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol”, RFC 2131, Standard, March 1997.
[2] S. Alexander and R. Droms, “DHCP Options and BOOTP Vendor Extension”, RFC 2132, Standard, March 1997.
Footnote
1 Our internal self-test result shows that a Windows 7 client PC does NOT send a DHCP Release message even after a normal log-off (power off). Thus, the client PC releases the allocated IP address to the DHCP server upon the expiration of the specified lease time.
Appendix A - Format of DHCP Messages in IP Address Allocation/Lease Procedure
DHCP Discover Message
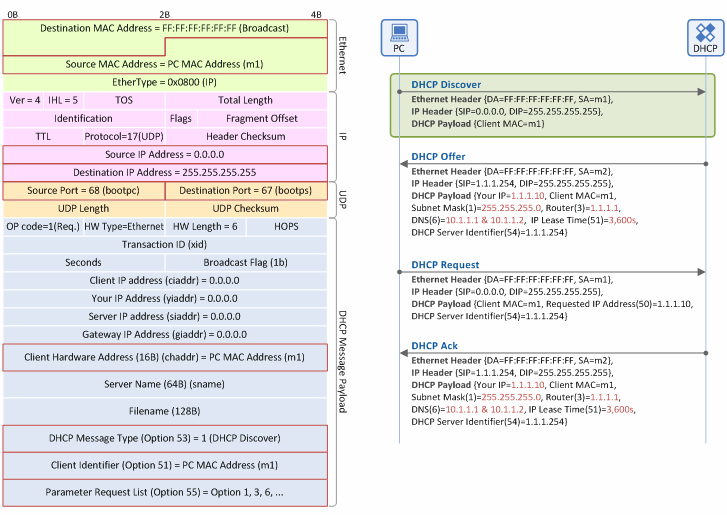
Figure 6. IP address allocation/lease procedure: DHCP Discover message
Ethernet Header
- Destination MAC Address: As the client is NOT aware of the MAC address of a DHCP server, it floods a DHCP Discover message on the Ethernet network using a broadcast MAC address (0xFFFFFFFFFFFF).
- Source MAC Address: The source MAC address on the Ethernet is always the address of a packet sender. Thus, this field is the MAC address of the client (m1).
- EtherType: Indicates that the header is followed by an IP packet (IP=0x0800, ARP=0x0806, etc).
IP Header
- Protocol ID: Indicates that the header is followed by a UDP packet (UDP=17, TCP=6, etc).
- Source IP Address: Is set to 0.0.0.0 because no IP address is allocated to the client.
- Destination IP Address: The client is NOT aware of the IP address of a DHCP server so it floods a DHCP Discover message over the IP network using a broadcast IP address (255.255.255.255).
UDP Header
- Source Port: Indicates that the DHCP message sender is the DHCP client (68=BOOTP Client), so the client always sends the message with “Source Port=68”.
- Destination Port: Indicates that the DHCP message receiver is the DHCP server (67=BOOTP Server), so the server always sends the message with “Destination Port=67”.
DHCP Message Payload
- Client MAC Address (chaddr): The MAC address of the client (m1).
- DHCP Message Type (option 53): Indicates that the DHCP message type is “DHCP Discover” (Value=1).
- Client Identifier (option 51): Serves as an indicator to distinguish clients, and generally contains the MAC address of the client (m1). The DHCP server distinguishes one client from another based on the values in this field.
- Parameter Request List (option 55): Contains the network information list (DHCP option List) that the client needs to obtain from the DHCP Server. For example, it requests subnet mask, default GW IP address, DNS IP address and so on.
DHCP Offer Message
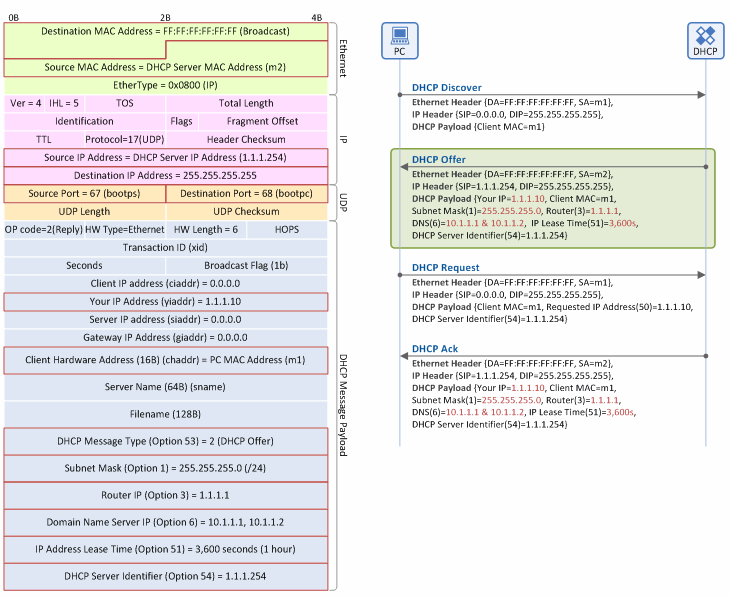
Figure 7. IP address allocation/lease procedure: DHCP Offer message
Ethernet Header
- Destination MAC Address: The DHCP server broadcasts a DHCP Offer message over the Ethernet network.
- Source MAC Address: The source MAC address on the Ethernet is always the address of a packet sender. Thus, this field is the MAC address of the client (m2).
IP Header
- Source IP Address: The IP address of a DHCP server (1.1.1.254)
- Destination IP Address: As the client is NOT aware of the IP address of the DHCP server, it floods a DHCP Discover message over the IP network using a broadcast IP address (255.255.255.255).
UDP Header
- Source Port: Indicates that the DHCP message sender is the DHCP server, so the server always sends the message with “Source Port=67”.
- Destination Port: Indicates that the DHCP message receiver is the DHCP client, so the client always sends the message with “Destination Port=68”.
DHCP Message Payload
- Your IP Address (yiaddr): The IP address to be used by the client (1.1.1.10).
- Client MAC Address (chaddr): The MAC address of the client (m1).
- DHCP Message Type (option 53): Indicates that the DHCP message type is “DHCP Offer” (Value=2).
- Subnet Mask (option 1): The subnet mask to be used by the client (255.255.255.0 (/24)).
- Router IP (option 3): The IP address (1.1.1.1) of the default gateway (the first router or L3 switch seen by the client to get to the Internet).
- Domain Name Server IP (option 6): The IP address of the DNS server to be used by the client. Normally, it provides two IP addresses, primary DNS IP address (10.1.1.1) and secondary DNS IP address (10.1.1.2), together.
- IP Address Lease Time (option 51): The lease time during which the client is allowed to use the IP address allocated by DHCP server (3,600 sec. (1 hour)). At the mid-point of the lease time (30 minutes), the client begins its IP address renewal procedure.
- DHCP Server Identifier (option 54): The IP address of the DHCP server that sent the DHCP Offer message (1.1.1.254). In case multiple DHCP servers on the same subnet send DHCP Offer messages to the client, the client distinguishes servers based on the values in this field.
DHCP Request Message
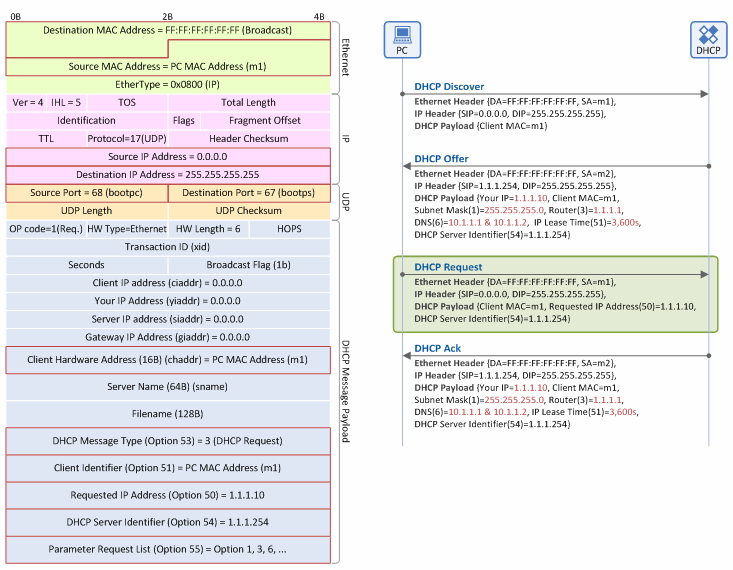
Figure 8. IP address allocation/lease procedure: DHCP Request message
Ethernet Header
- Destination MAC Address: As the client is NOT aware of the MAC address of a DHCP server, it floods a DHCP Request message over the Ethernet network using a broadcast MAC address (0xFFFFFFFFFFFF) in order to inform all the DHCP servers of which DHCP server is selected by the client.
- Source MAC Address: The source MAC address on the Ethernet is always the address of a packet sender. Thus, this field is the MAC address of the client (m1).
IP Header
- Source IP Address: Is set to 0.0.0.0 because no IP address is allocated to the client.
- Destination IP Address: It floods a DHCP Request message over the IP network using a broadcast IP address (255.255.255.255) in order to deliver the DHCP Request message to all the DHCP servers on the same subnet.
UDP Header
- Source Port: Indicates that the DHCP message sender is the DHCP client (68=BOOTP Client).
- Destination Port: Indicates that the DHCP message receiver is the DHCP server (67=BOOTP Server).
DHCP Message Payload
- Client MAC Address (chaddr): The MAC address of the client (m1).
- DHCP Message Type (option 53): Indicates that the DHCP message type is “DHCP Request” (Value=3).
- Client Identifier (option 51): Serves as an indicator to distinguish clients, and generally contains the MAC address of the client (m1). The DHCP server distinguishes one client from another based on the values in this field.
- Requested IP Address (option 50): The IP address (yiaddr=1.1.1.10) received through the DHCP Offer message from the DHCP server. This is intended to re-send the IP address to the DHCP server in order to verify if the IP address is valid (In normal operation, the DHCP server allocates the IP address to the client through the DHCP Ack message).
- Parameter Request List (option 55): Contains the network information list (DHCP option List) that the client needs to obtain from the DHCP Server. For example, it requests subnet mask, default GW IP address, DNS IP address and so on.
DHCP Ack Message
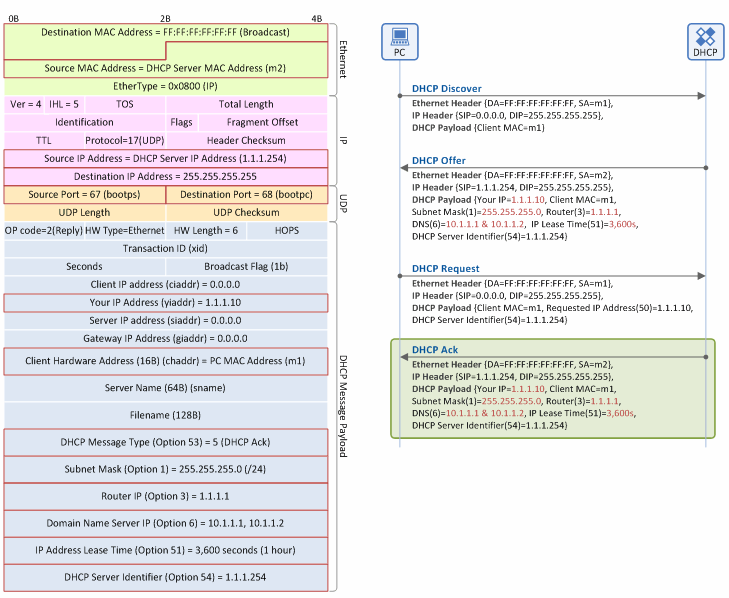
Figure 9. IP address allocation/lease procedure: DHCP Ack message
Ethernet Header
- Destination MAC Address: The DHCP server broadcasts a DHCP Ack message over the Ethernet network to reach the client.
- Source MAC Address: The source MAC address on the Ethernet is always the address of a packet sender. Thus, this field is the MAC address of the DHCP server (m2).
IP Header
- Source IP Address: The IP address of DHCP server (1.1.1.254).
- Destination IP Address: As the client is NOT aware of the IP address of the DHCP server, it floods a DHCP Discover message over the IP network using a broadcast IP address (255.255.255.255).
UDP Header
- Source Port: Indicates that the DHCP message sender is the DHCP server, so the server always sends the message with “Source Port=67”.
- Destination Port: Indicates that the DHCP message receiver is the DHCP client, so the client always sends the message with “Destination Port=68”.
DHCP Message Payload
- Your IP Address (yiaddr): The IP address to be used by the client (1.1.1.10).
- Client MAC Address (chaddr): The MAC address of the client (m1).
- DHCP Message Type (option 53): Indicates that the DHCP message type is “DHCP Ack” (Value=5).
- Subnet Mask (option 1): The subnet mask to be used by the client (255.255.255.0 (/24)).
- Router IP (option 3): The IP address (1.1.1.1) of the default gateway (the first router or L3 switch seen by the client to get to the Internet).
- Domain Name Server IP (option 6): The IP address of DNS server to be used by the client. Normally, it provides two IP addresses, primary DNS IP address (10.1.1.1) and secondary DNS IP address (10.1.1.2), together.
- IP Address Lease Time (option 51): The lease time during which the client is allowed to use the IP address allocated by DHCP server (3,600 sec. (=1 hour)). At the mid-point of the lease time (30 minutes), the client begins its IP address renewal procedure.
- DHCP Server Identifier (option 54): The IP address of the DHCP server that sent the DHCP Offer message (1.1.1.254). In case that multiple DHCP servers on the same subnet send DHCP Offer messages to the client, the client distinguishes servers based on the values in this field.
Appendix B - Format of DHCP Messages in IP Address Renewal Procedure
DHCP Request Message
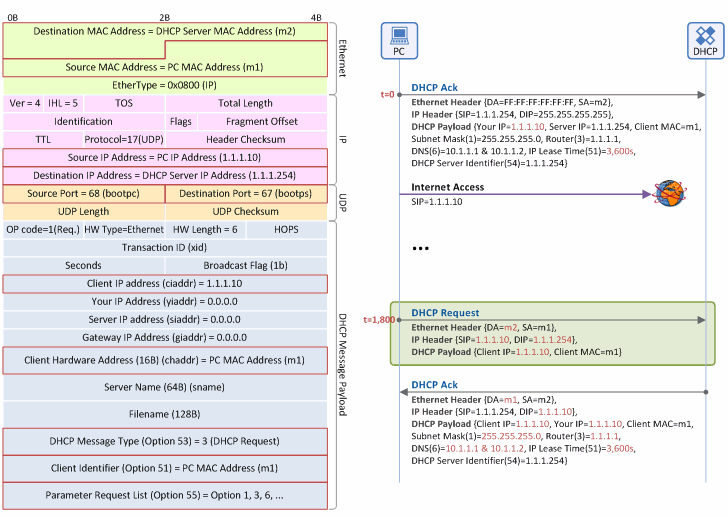
Figure 10. IP address renewal procedure: DHCP Request message
Ethernet Header
- Destination MAC Address: The MAC address of the DHCP server (m2)- Unicast type message over the Ethernet
- Source MAC Address: The source MAC address on the Ethernet is always the address of a packet sender. Thus, this field is the MAC address of the client (m1)
- EtherType: Indicates that the header is followed by an IP packet (IP=0x0800, ARP=0x0806, etc).
IP Header
- Protocol ID: Indicates that the header is followed by a UDP packet (UDP=17, TCP=6, etc).
- Source IP Address: The client IP address.
- Destination IP Address: The DHCP server IP address.
UDP Header
- Source Port: Indicates that the DHCP message sender is the DHCP client (68=BOOTP Client), so the client always sends the message with “Source Port=68”.
- Destination Port: Indicates that the DHCP message receiver is the DHCP server (67=BOOTP Server), so the server always sends the message with “Source Port=67”.
DHCP Message Payload
- Client IP Address (ciaddr): The IP address (1.1.1.10) of the client in use (intended to extend a lease time)
- Client MAC Address (chaddr): The MAC address of the client (m1)
- DHCP Message Type (option 53): Indicates that the DHCP message type is “DHCP Request” (Value=3).
- Client Identifier (option 51): Serves as an indicator to distinguish clients, and generally contains the MAC address of the client (m1). The DHCP server distinguishes one client from another based on the values in this field.
- Parameter Request List (option 55): Contains the network information list (DHCP option List) that the client needs to obtain from DHCP Server. For example, it requests subnet mask, default GW IP address, DNS IP address and so on.
DHCP Ack Message
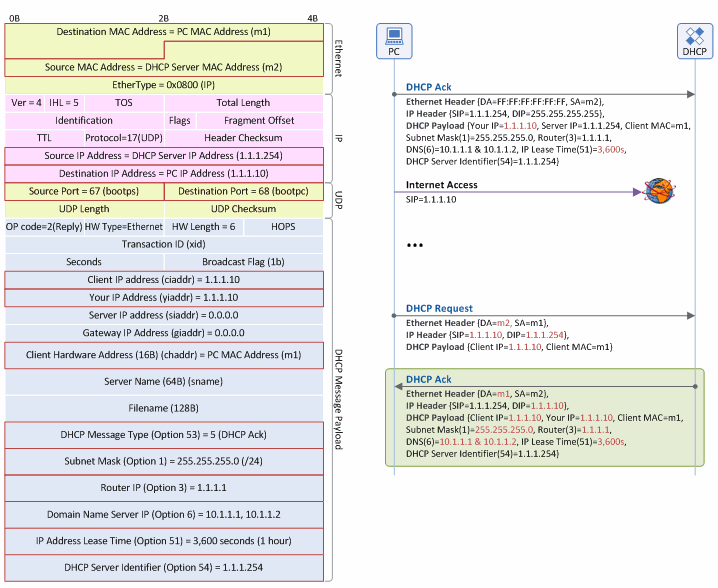
Figure 11. IP address renewal procedure: DHCP Ack message
Ethernet Header
- Destination MAC Address: The MAC address of the DHCP client (m1) - Unicast type message over the Ethernet.
- Source MAC Address: The source MAC address on the Ethernet is always the address of a packet sender. Thus, this field is the MAC address of the DHCP server (m2)
IP Header
- Source IP Address: The IP address of DHCP server (1.1.1.254)
- Destination IP Address: The IP address of DHCP client (1.1.1.10) - Unicast type message over the Ethernet.
UDP Header
- Source Port: Indicates that the DHCP message sender is the DHCP server, so the server always sends the message with “Source Port=67”.
- Destination Port: Indicates that the DHCP message receiver is the DHCP client, so the client always sends the message with “Destination Port=68”.
DHCP Message Payload
- Client IP Address (ciaddr): The IP address (1.1.1.10) of the client in use (intended to extend a lease time)
- Your IP Address (yiaddr): The IP address (of which lease extension is permitted by the DHCP server) to be used by the client (1.1.1.10).
- Client MAC Address (chaddr): The MAC address of the client (m1).
- DHCP Message Type (option 53): Indicates that the DHCP message type is “DHCP Ack” (Value=5).
- Subnet Mask (option 1): The subnet mask to be used by the client (255.255.255.0 (/24)).
- Router IP (option 3): The IP address (1.1.1.1) of the default gateway (the first router or L3 switch seen by the client to get to the Internet).
- Domain Name Server IP (option 6): The IP address of DNS server to be used by the client. Normally, it provides two IP addresses, primary DNS IP address (10.1.1.1) and secondary DNS IP address (10.1.1.2), together.
- IP Address Lease Time (option 51): The lease time during which the client is allowed to use the IP address allocated by the DHCP server (3,600 sec. (1 hour)). At the mid-point of the lease time (30 minutes), the client begins its IP address renewal procedure.
- DHCP Server Identifier (option 54): The IP address of the DHCP server that sent the DHCP Offer message (1.1.1.254). The client stores information about from which DHCP server the client leased its IP address, and then uses the IP address for IP renewal or IP release procedures.
Appendix C - Format of DHCP Messages in IP Address Release Procedure
DHCP Release Message
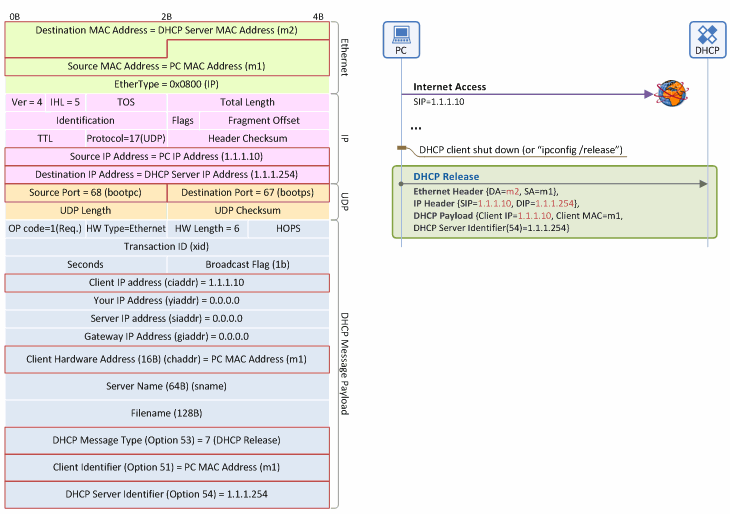
Figure 12. IP address release procedure: DHCP Release message
Ethernet Header
- Destination MAC Address: The MAC address of the DHCP server (m2) - Unicast type message over the Ethernet
- Source MAC Address: The source MAC address on the Ethernet is always the address of a packet sender. Thus, this field is the MAC address of the client (m1).
- EtherType: Indicates that the header is followed by an IP packet (IP=0x0800, ARP=0x0806, etc).
IP Header
- Protocol ID: Indicates that the header is followed by a UDP packet (UDP=17, TCP=6, etc).
- Source IP Address: The client IP address (1.1.1.10).
- Destination IP Address: The DHCP server IP address (1.1.1.254 ) - Unicast type message over the Ethernet
UDP Header
- Source Port: Indicates that the DHCP message sender is the DHCP client (68=BOOTP Client), so the client always sends the message with “Source Port=68”.
- Destination Port: Indicates that the DHCP message receiver is the DHCP server (67=BOOTP Server), so the server always sends the message with “Source Port=67”.
DHCP Message Payload
- Client IP Address (ciaddr): The IP address (1.1.1.10) of the client in use (Intended to return to DHCP server)
- Client MAC Address (chaddr): The MAC address of the client (m1)
- DHCP Message Type (option 53): Indicates that the DHCP message type is “DHCP Release” (Value=7).
- DHCP Server Identifier (option 54): The IP address of the DHCP server that sent the DHCP Offer message (1.1.1.254).
ijust can say thanks,very thanks,it was complete article
Excellent article. Clearly put. Great work. Thank you.
Nice article to understand.
very good article. one place to viist to understand DHCP in detail...
An amazing article, really well written. Keep up the good work. I recommend this to all network engineer. This is the only article series where I found everything I need in one place.
Very clear, nice article
Very good informative article.
Hi,
Article is very clear. But I have two doubts.
Doubt 1:
========
Asssume that client got the ipc at 1pm with lease time of 1hr. So, Till 2pm we can use this ip. now the client will request again at 1.30pm for renewal. Now again assume that we got one hr in this renewal process. Here comes my question is, already we have acess for the time 1.30pm to 2pm. Now after renewal(1 hr). So now our ip is allowed till 3pm or time reset from 1.30pm to 2.30 pm ??
If our ip is allowed only till 2.30 then looks like we got only half an hour extra time(from 2pm to 2.30pm).
Doubt 2:
========
In the DHCP paylod, we have client Identifer field(option 51) & also Client Hardware address. For DHCP Request we are filling client MAC in both place. What is the specific purpose.
If no specific reason, then wy we need to fill twice??
Could you clarify my doubt?
On D-1: I think it is obvious that at 1:30 you will renew for 1 hour until 2:30. Renewal starts at 1:30 and not at 1:59 because operation may fail and need retry and we don't need network intterruption even for 1 second. In other words, the real lease time is half hour and DHCP server gives twice time the chance to get new lease.
Thank you very much for the explanation, You rock!
very good description
Hi , Just curious , you are using router ip address 1.1.1.1 --> is this as a gateway ? because in a header i saw the gateway ip address is 0.0.0.0. thanks
Explained perfectly. I've read about this on wikipedia formerly but didn't understand correctly but here understood completely
isn't the DHCP offer and Ack unicast ???
DHCP already have - siaddr and giaddr fields right; but why do they use options field to provide router IP and DHCP IP when they already have those fields?
Moreover, I have captured the packets in Wireshark; could see the same thing; also observed that it lacks options other than 53 and 54 (here in my case my DHCP server= gw=dns); so is there any field which when set to 1 or 0 indicates that everything is same?
Very good explanation. Thank you for your detailed descriptions.
Easy to understand the background on how DHCP works
Just working on a question regarding netmasks and DHCP. Should a client in renew state recognise and deploy a modified netmask in the ACK message? We are facing the question of how to extend networks "on the fly" and would like to avoid restarting the complete process.
in the last step, internet access with SIP=1.1.1.10 is impossible, because it is just a private IP address. NATTing is required.
Wow... great article. What I miss in this article, is the following case:
If the unicast DHCP RENEWAL process fails because of a unicast connectivity issue, then after T2 (87.5% of the lease time) the client it will do the renewal or rebinding with broadcast until the lease expires. This process is called rebinding. (https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/previous-versions/windows/it-pro/windows-2000-server/cc958935(v=technet.10)?redirectedfrom=MSDN)
So good, cheers bro!